What are bed bugs?
Bed bugs are small insects that feed on the blood of animals. Adult bed bugs are oval, wingless and rusty red colored, and have flat bodies, antennae and small eyes. At 3/16-inch long, they are visible to the naked eye, but often hide in cracks and crevices. When bed bugs feed, their bodies swell and become a brighter red. Bed bugs feed primarily on the blood of humans, usually at night when people are sleeping. Bed bugs cannot jump or fly.
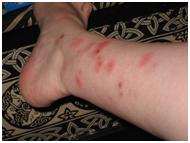
What does a bed bug bite feel and look like?
Typically, the bite is painless and rarely awakens a sleeping person. However, it can produce large, itchy welts on the skin. Welts from bed bug bites do not have a red spot in the center – those welts are more characteristic of flea bites.
What is the treatment for bed bug bites?
It is important to note that bed bugs have not been shown to transmit any human diseases. Suggestions to treat the bites include:
- Resist the urge to scratch. Scratching may only intensify the itch and lead to the bite becoming infected
- Wash the bites with soap and water
- Use over-the-counter antihistamine and corticosteroid medications to reduce allergic reactions
- Use antibiotic products to prevent infection, and see a health care provider if you develop an infection.
Are bed bugs dangerous?
Although bed bugs may be a nuisance to people, they do not spread disease. They are known to cause allergic reactions from their saliva in sensitive people.
How long do bed bugs live?
The typical life span of a bed bug is about 10 months. They can survive for weeks to months without feeding.
Who is at risk of getting bed bugs?
Anyone who comes in direct contact with bed bugs can carry them into their homes in clothes, second hand beds and bedding, furniture, or suitcases. Infestations are not tied to unsanitary living conditions; even world-class hotels have reported bed bug problems.
How are bed bugs spread?
Bed bugs may be found in homes, motels, hostels, movie theaters, transportation depots, and rest rooms. They may be accidentally moved with clothes, suitcases, furniture, and other personal items. Bed bugs may also be transported in second-hand or rental furniture. Bed bugs do not fly or jump, but they move quickly over floors, walls, ceilings, and furniture.
How do I know if I have bed bugs?

If you have bed bugs, you may have itchy welts on your skin. You may also see the bed bugs themselves, small bloodstains on sheets from crushed bed bugs, or tiny dark spots from bed bug droppings in areas where the bugs hide.
Bed bugs often hide in or near beds and mattresses and daybed covers. In more severe infestations, bed bugs may spread to cracks and crevices in bed frames and box springs; behind headboards; inside nightstands; behind baseboards, window and door casings, pictures, and moldings; and in nearby furniture, loosened wallpaper, and cracks in plaster and flooring. Bed bugs may also hide in piles of books, papers, boxes, and other clutter near sleeping areas.
What do I do if I suspect bed bugs?
Educate yourselves about bed bugs, conduct self inspections, and follow recommended treatment methods from a reputable source. The Environmental Health Services section of the Cabell County Health Department is a good resource for students living in off-campus housing.
If you live in a dormitory at Marshall, contact your Residence Advisor or Residence Director and inform them of the suspected infestation.
Find out where bed bugs are hiding
Use a bright flashlight to examine bedroom furniture for bed bugs or their dark droppings.
You should check:
- Behind the headboard
- In the seams and tufts of the mattress, and around or inside the box spring (may require removal of fabric covering the bottom)
- Along the crevices of bedroom baseboards, especially the baseboard area below the headboard
- Inside and around nightstands
- Behind or within other items or cracks in the bedroom (for example, window and door casings, pictures, and moldings, nearby furniture, loosened wallpaper, and cracks in plaster and partitions, and clutter)
- Along baseboards, along and under the edge of wall-to-wall carpeting
In addition to using a flashlight, carefully aiming a hot hair dryer into these crevices while looking will help force bed bugs out.
Treatment
- Understand that it may require the assistance of a licensed pest management professional
- Washing and machine drying bedding, garments, and other launder-able items will kill bed bugs
- Placing items like toys, shoes, backpacks, etc. in a clothes dryer set at medium to high heat for 10 to 20 minutes is effective (120 degrees F minimum)
- Items which cannot be put in a washer or dryer can sometimes be de-infested by wrapping in a sealed black trash bag and placing them outdoors in a hot, sunny location, closed vehicle, etc. for at least a day. Packing fewer items per bag will make it harder for the bugs to find cooler places to hide. Use a thermometer to ensure an internal temperature of at least 120°F.
- Bed bugs also will succumb to cold temperatures below 32°F, but freezing temperatures must be maintained for several days.
- General housecleaning measures, such as vacuuming floors and surfaces, seldom reaches the places where bed bugs hide. Targeted vacuuming of infested harborages, however, can help remove some of the bugs before treatment with insecticides. Bed bugs and especially the eggs can be difficult to dislodge. Optimum results will be achieved by moving and scraping the end of the suction wand along infested areas such as seams and fabric folds of beds and sofas, and the perimeter edge of wall-to-wall carpets. Afterward, dispose of the vacuum contents in a sealed trash bag.
- Infected matresses and box springs can be encased in a protective cover labeled for allergy relief. Trapped bed bugs will eventually die, however it may take up to a year or more. Any tears or rips in the cover must be immediately sealed to prevent release of the bugs.
- At times it may be necessary to throw out infested items, especially beds and upholstered furniture.
- When infested items are discarded, bagging or wrapping them prevents dislodgement of bugs en route to the trash.
- Knowledgeable pest control firms are able to advise clients on what can stay and what should go.
- While the aforementioned measures are helpful, insecticides are important for bed bug elimination. Professionals treat using a variety of low-odor sprays, dusts and aerosols. Baits designed to control ants and cockroaches are ineffective. Application entails treating all areas where the bugs are discovered or tend to crawl or hide. This may take hours of effort and follow-up visits are usually required.
- Some pest control firms also employ commercial steamers or rapid freezing equipment to treat areas where bed bugs are found or suspected. Used correctly, they kill both bugs and eggs on contact. Neither method, however, affords residual protection against bed bugs which may have been missed.
How can I prevent bed bugs?
Avoid purchasing used furniture, especially beds, mattresses, couches, and upholstered chairs.
Keep suitcases off the floor, on a luggage stand, tabletop, or other hard surface. Should you experience itchy welts suggestive of bed bugs while traveling, upon returning home immediately wash and dry all items and steam treat or discard the suitcase.
If a roommate has bed bugs, you may try using double-sided tape on the bed legs, or coating the legs of beds with petroleum jelly or so bed bugs will not be able to climb onto the bed. Putting the legs of the bed frame in empty cans or glass jars may also help since bed bugs cannot fly or jump.